
Creating an energy efficient smart home isn’t just about being eco-friendly, it’s also about saving money and adding convenience to your life. As climate concerns grow and energy costs rise, Canadian homeowners are increasingly turning to smart technologies and energy-saving habits to reduce their environmental footprint and utility bills. Smart home technology is playing a key role in this shift. From intelligent thermostats that learn your routine to lighting systems that respond to your presence, an energy efficient smart home not only reduces energy consumption but also enhances comfort and convenience.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to save energy using smart home tech and which smart home devices are best for energy efficiency. You’ll also receive practical tips to reduce electricity bills and product recommendations and insights into energy efficient appliances.
Let’s explore how to transform your home into a greener, smarter, and more efficient living space.
Why energy efficiency in smart homes matters

Energy efficiency is important for numerous reasons.
Environmental impact: reducing carbon footprint
A significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions comes from residential energy use. Heating, cooling, and powering our homes contribute to global warming. Making your home more energy efficient helps reduce carbon emissions, slows climate change, and protects natural resources.
Financial benefits: lowering electricity bills
Energy-efficient upgrades like switching to LED lighting or using energy star appliances can lower your monthly energy bills. Over time, these savings can add up significantly, especially when combined with smart home automation that helps you monitor and control usage.
Debunking the myth: “tech consumes more energy”
It’s a common misconception that smart tech uses more energy. In reality, devices like smart thermostats and plugs are designed to save energy by reducing waste and running only when needed. They’re investments that pay off in efficiency and savings. They allow you to control things like lights and thermostats remotely, turning things on and off, and adjusting levels. Some even do this autonomously as they learn your habits or sense your presence.
Types of smart home products for energy efficiency
Smart technology can touch every corner of your home. Here’s a quick breakdown of the main categories:
- Lighting: Smart bulbs and switches
- Climate control: Thermostats, fans, portable air conditioners, smart blinds
- Appliances: Energy-efficient smart washers, dryers, and fridges
- Plugs & sensors: Smart plugs, power strips, surge protectors, water sensors
- Automation & monitoring tools: Apps, voice assistants, smart hubs
Energy efficient smart devices to transform your home
Smart lighting solutions
Lighting is one of the easiest and most impactful upgrades you can make to your home to make it more energy efficient. LED bulbs are more efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs, and they last far longer, too. The upfront cost is more but it’s worth it in the long run.
Benefits of LED vs. traditional bulbs
| Feature | LED Bulbs | Incandescent Bulbs |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | 75% less | High |
| Lifespan | Up to 25,000 hours | ~1,000 hours |
| Heat Emission | Very low | High |
| Cost Over Time | Lower | Higher |
Smart lighting offers more than just lower energy usage, these bulbs, strips, and other types of smart lighting enable smarter control over your home’s lighting environment. Built-in features like scheduling let you program lights to turn off during the day or late at night, automatically saving power. Geofencing can sync with your phone’s location to ensure lights switch off when no one’s home. Motion sensors detect movement and only illuminate when needed, perfect for hallways, bathrooms, or outdoor areas. For deeper energy savings and comfort, dimmers and adjustable colour temperatures help fine-tune brightness and warmth, reducing power usage while setting the perfect mood for every room. You can also reduce eye strain and create ambiance that supports your circadian rhythm.
Pro Tip: Opt for dimmable smart bulbs and use warm tones in the evening to improve relaxation and sleep quality. Many smart lighting apps also let you group lights by room, adjust brightness remotely, and integrate voice controls. This makes it easier than ever to manage energy use.
Smart thermostats

Smart thermostats from brands like Google Nest and Ecobee are at the forefront of home energy efficiency. They don’t just let you adjust the temperature from your phone, they actively learn your daily habits and automatically adjust your HVAC system to align with your lifestyle. For instance, if you typically lower the heat at night and raise it in the morning, your thermostat will start making those changes automatically.
Beyond remote control, these devices save energy through adaptive learning and automation. Over time, they gather data about your usage patterns and fine-tune your heating and cooling schedule to avoid unnecessary energy use. They also monitor your home’s energy consumption, providing insights and suggestions to help you save more.
Geofencing is another standout feature. It uses your smartphone’s location to detect when you’re home or away. When you leave, the thermostat switches to an eco mode to conserve energy, and it resumes your preferred settings when you’re nearby so your home is always comfortable when you walk in.
Additionally, smart thermostats factor in weather data to adjust your settings automatically based on outdoor temperatures, humidity, and seasonal changes. This ensures your system isn’t working harder than it needs to. For example, if it’s an unusually sunny winter day, the thermostat may lower your heating slightly to take advantage of passive solar warmth.
Together, these features make smart thermostats powerful tools for creating an energy efficient smart home, offering comfort, control, and significant energy savings with minimal effort.
Smart plugs & power strips
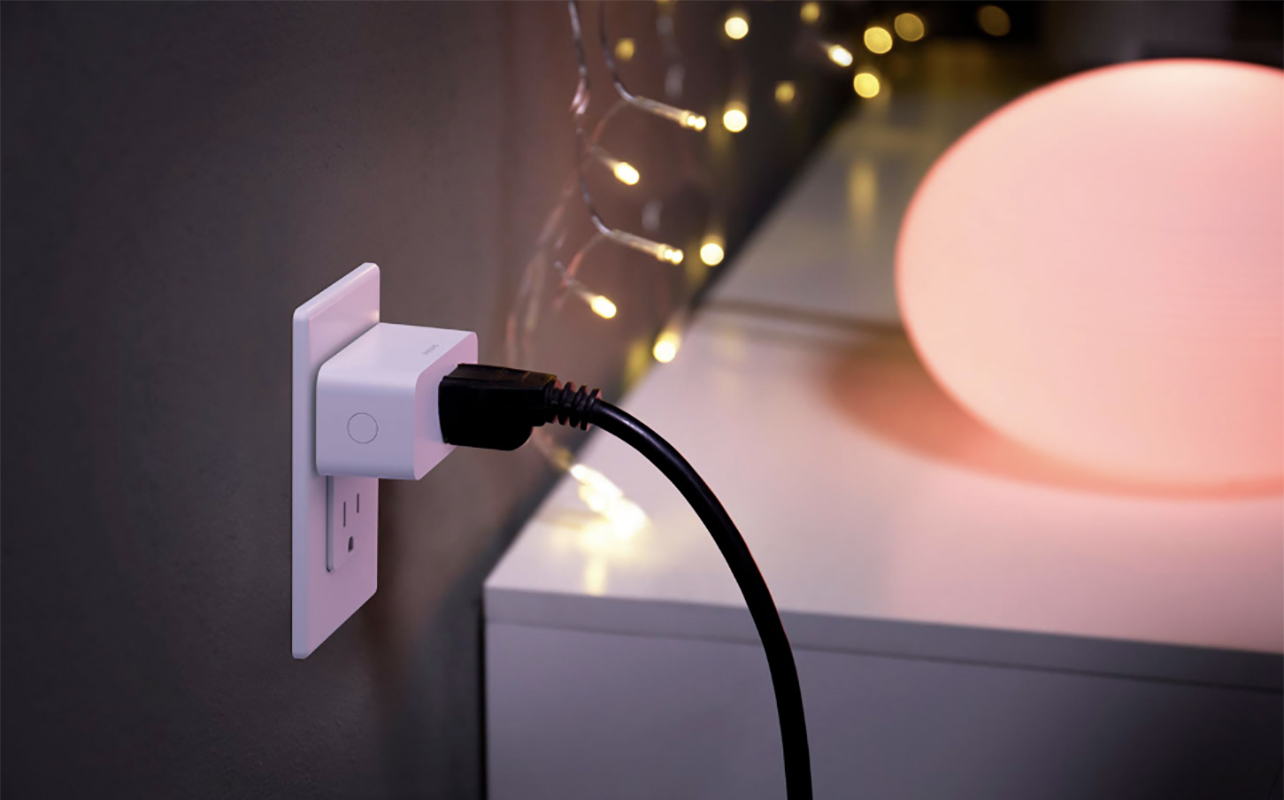

Smart plugs and power strips are one of the easiest and most affordable ways to make your home more energy efficient. They allow you to turn traditional electronics into smart devices by enabling remote control and automation. For example, a regular coffee maker or fan becomes programmable with a smart plug. You can schedule it to turn off automatically after use or power on before you wake up.
One of the most valuable benefits of smart plugs is their ability to combat phantom power, standby energy used by electronics that remain plugged in even when turned off.
Smart plugs are incredibly versatile. They can be used with indoor appliances like lamps, computers, and coffee makers, or outdoor setups like patio heaters and holiday lights. However, not all plugs are made for all conditions. Here’s a simple comparison:
| Feature | Indoor Smart Plug | Outdoor Smart Plug |
|---|---|---|
| Weatherproof Design | No | Yes |
| Typical Use Cases | Lamps, electronics | Patio lights, garden tools |
| Safety Certification | Basic indoor ratings | IP-rated for water and dust resistance |
| Installation Requirements | Standard indoor outlets | Compatible with weather-safe outlets |
| Scheduling | Yes | Yes |
| Voice Control | Yes | Yes |
| Power Monitoring | Some models | Some models |
Smart power strips take it a step further by offering multiple outlets with surge protection, energy monitoring, and auto shut-off for unused devices. Many advanced models even let you control each outlet individually via an app. They give you detailed insight into your energy usage and helping you fine-tune your consumption habits.
Water leak sensors
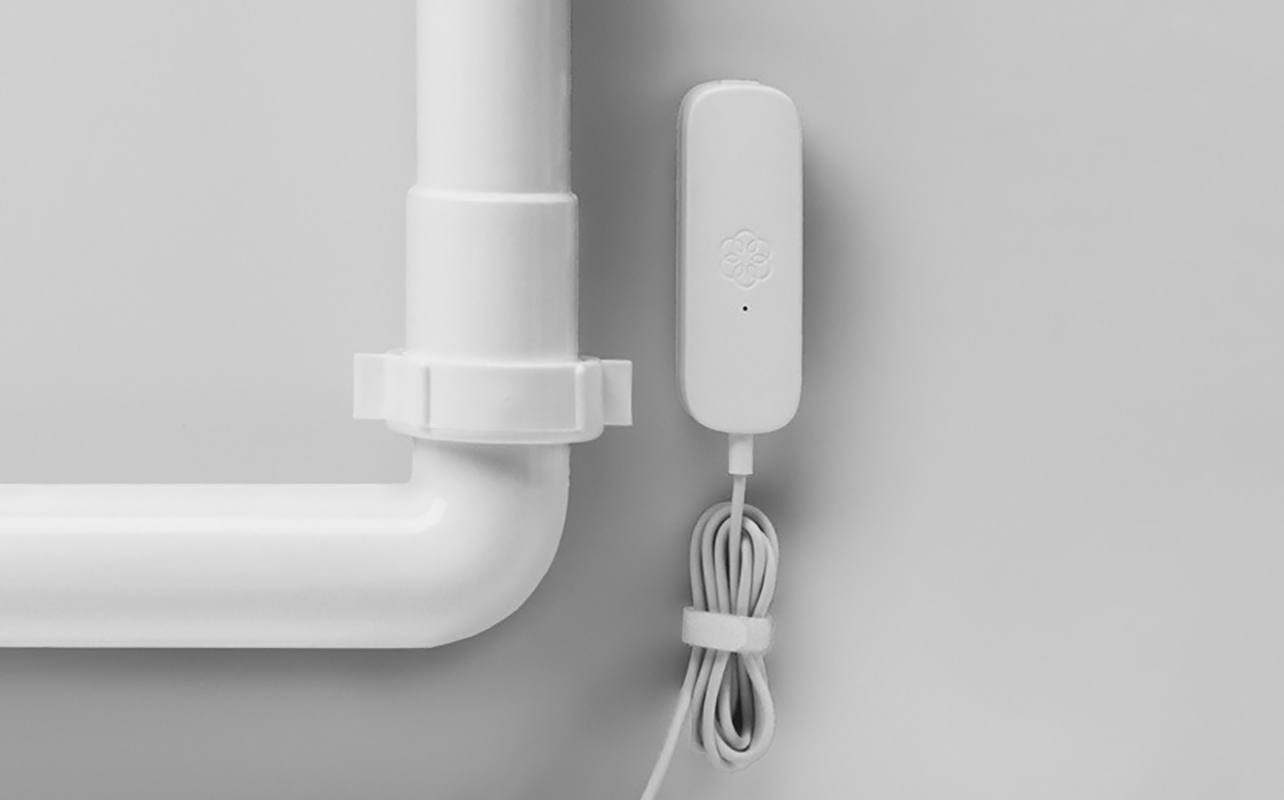

Water waste = energy waste, especially when it impacts your heating system or causes damage that leads to inefficient operation of other appliances. Smart water leak sensors are small, battery-powered devices that detect moisture in areas prone to leakage, such as under sinks, behind washing machines, or near water heaters.
These sensors alert you immediately through your smartphone, allowing for quick action before damage or water waste escalates. Many of them integrate with smart shutoff valves, automatically cutting off the water supply when a leak is detected.
This early detection not only prevents costly water damage but also preserves energy by keeping water heaters and other affected systems operating efficiently. For example, catching a slow leak in your hot water tank early can save you hundreds in both repair costs and energy waste over time.
Upgrade to energy efficient appliances

Modern appliances do far more with far less energy, especially those certified with the ENERGY STAR label.
Large appliances
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Appliance | Energy Saving Features |
| Refrigerator | Inverter compressor, Wi-Fi alerts, smart compartments, advanced cooling |
| Washer/Dryer | Cold wash, load sensing, smart scheduling |
| Dishwasher | Eco cycles, smart sensors, delayed start, usage tracking |
Refrigerators
Energy Star-rated refrigerators offer advanced insulation, inverter compressors, and compartmentalized cooling systems that use up to 15% less energy than non-certified models. Some models even include door-in-door compartments to minimize temperature loss when you access frequently used items. Many also offer smart features such as Wi-Fi connectivity, letting you monitor energy use, set cooling preferences, and receive alerts if the door is left open or the internal temperature rises unexpectedly.
Washers & Dryers
Smart washers and dryers come equipped with energy-saving features that go far beyond the basics. Cold water cycles significantly reduce energy consumption since heating water is one of the largest contributors to energy use in laundry. Many models also offer smart scheduling features, allowing you to run loads during off-peak energy hours when rates are lower. High-speed spin cycles are another clever addition. They remove more water from clothes, which reduces the amount of time and energy needed for drying. Smart sensors further enhance efficiency by automatically adjusting the cycle time and water levels based on the load’s weight and soil level, avoiding overuse of water or electricity.
Dishwashers
Modern dishwashers have become highly intelligent and efficient. Eco cycles are designed to use less water and electricity without compromising cleanliness. Soil sensors in smart dishwashers analyze how dirty the dishes are and adjust cycle intensity and duration accordingly. Delay start options enable you to run the dishwasher during lower electricity rate periods, which can save money and energy. Advanced models even feature smart connectivity, providing maintenance alerts, cycle tracking, and the ability to start or stop a load remotely, ensuring you only run cycles when absolutely needed.
Small appliances

There are both small appliances that are smart as well as ways to use them to help save energy.
Air fryers & multicookers
Air fryers and multicookers are increasingly popular not just for their convenience, but for their energy efficiency. These compact kitchen appliances use rapid air circulation or sealed pressure cooking to prepare meals faster and with less electricity compared to conventional ovens or stovetops. They also require minimal preheating, reducing energy waste further. Because many models combine multiple cooking functions like baking, steaming, sautéing, and pressure cooking, you can replace several single-use appliances, saving space and energy in one go.
Smart kettles & coffee makers
Smart kettles and programmable coffee makers help eliminate idle heating, which is a common energy drain in most kitchens. Many models come with scheduled brewing and temperature control settings, ensuring you heat only what you need, when you need it. Used in combination with smart plugs, you can automate start times to align with your morning routine or turn off the appliance if it’s accidentally left on. By customizing usage and avoiding overheating, you prevent unnecessary power consumption and extend the life of your device.
Small habit changes with appliances
Beyond appliances themselves, changing your cooking habits can make a noticeable impact on your home’s overall energy efficiency. For instance, using lids on pots can retain heat and cook food faster. Cooking multiple meals at once or batch-cooking reduces the need to use large appliances several times a day. Using the microwave or toaster oven for smaller portions instead of heating a full-sized oven is another easy win. Additionally, matching the size of your cookware to the burner size on your stove can prevent energy from being wasted. Over time, these small adjustments add up to measurable energy savings.
By choosing energy efficient appliances and developing smarter cooking habits, you can lower your energy bills without compromising performance or convenience in the kitchen.
How to reduce power waste in your home
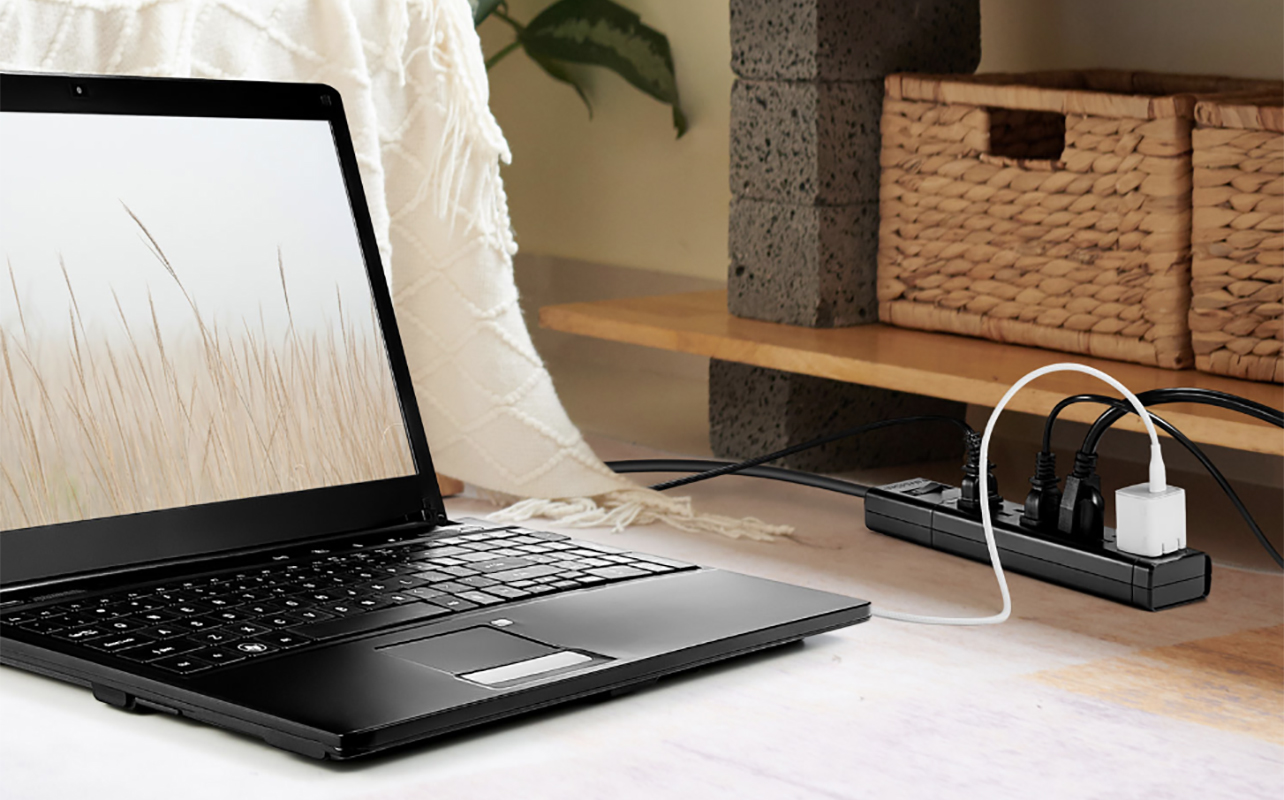

What is phantom power?
Phantom power, or standby power, refers to the electricity consumed by devices that remain plugged in but are not actively in use. These hidden energy drains can quietly add up over time, contributing to up to 10% of a home’s total energy usage. TVs, cable boxes, game consoles, printers, and kitchen appliances are some of the most common contributors.
Here’s a breakdown of typical phantom power usage:
| Device | Average Standby Use (W) | Annual Energy Cost (CAD) |
| Game Console (off mode) | 10 | ~$15 |
| Cable TV Box (idle) | 18 | ~$27 |
| Microwave (clock only) | 3 | ~$5 |
| Laptop Charger (plugged in) | 4 | ~$6 |
Tips to cut standby power
Reducing phantom load can be simple with the right habits and tools. Use smart power strips to turn off groups of devices at once. Unplug chargers and small appliances when not in use. Activate energy-saving settings on TVs, consoles, and computers, when available. Monitor usage with a home energy assessment or smart meter. Add occupancy sensors to automatically switch off lighting in unused rooms.
A combination of awareness and automation can significantly lower your overall energy footprint and cut unnecessary costs.
Automation and habits for long-term savings

Smart devices are most effective when integrated into your daily routines. By automating regular tasks, you reduce reliance on manual intervention and ensure consistent energy savings.
Set daily routines
Automate lighting, climate control, and device operation around your lifestyle. For example, schedule your thermostat to lower heating overnight or lights to switch off automatically during daylight hours.
Use voice assistants
Control devices with ease using smart speakers like Google Nest or Amazon Echo. Instead of searching for remotes or apps, a quick command can shut off multiple lights or adjust the temperature.
Combine smart devices
Link smart blinds with your thermostat to reduce cooling loads during summer. Use window sensors to trigger fans or turn off HVAC when windows are open. When devices work in tandem, your energy savings multiply. You can usually set up “scenes” in smart home control apps to control multiple devices at once with the press of a button or a simple voice command. Your “goodnight” scene, for example, might turn off all lights, activate the security camera, turn off the coffee maker, and shut down AV equipment.
Monitor and optimize
Most smart devices offer apps that provide real-time usage stats. Use these to track trends, identify wasteful behaviours, and tweak settings to get the most from your energy-saving ecosystem.
Activate vacation modes
Smart homes can detect prolonged inactivity and shift into energy-conserving states automatically. Thermostats, lights, and plugs can be adjusted collectively to minimize consumption while you’re away. Instead of leaving one light on in the home 24/7 all week so people think someone is there, set a timer so the living room light goes on every night at 8 p.m. and off at 10 p.m., for example.
Pro Tip: Use a central smart hub to coordinate all your devices. Whether you prefer Apple HomeKit, Google Home, or Amazon Alexa, a unified interface simplifies setup and amplifies your ability to create truly efficient routines. This also makes it easy to control everything from a single app.
Conclusion

Improving your home’s energy efficiency doesn’t mean overhauling everything at once. Small upgrades like swapping in smart bulbs or switching off phantom power build over time into meaningful savings. By investing in energy saving home improvements, choosing energy efficient appliances, and adopting smart home habits, you can create a more sustainable, cost-effective living environment. Remember: building an energy efficient home is not just good for your wallet, it’s a step toward a cleaner, smarter future. Going green isn’t just trendy, it’s smart living.
Ready to take the leap? Check out all types of smart home gear at Best Buy Online.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Do smart home devices really save energy?
Yes! They optimize power use through automation and reduce waste, especially with smart thermostats, lighting, and power strips. Studies from the U.S. Department of Energy confirm consistent savings when smart devices are used effectively.
How much can I save with a smart thermostat?
Savings vary, but studies show reductions of up to 15% on heating and cooling costs. That could mean hundreds of dollars per year depending on your home’s size and location. Some locations also provide rebates when you use energy efficient smart home devices like smart thermostats, so check with your local electricity company.
What’s the easiest smart device to start with?
Smart plugs and LED bulbs are the perfect first place to start. They’re affordable, simple to set up, and offer immediate savings. Plus, they can be controlled from your phone or voice assistant for added convenience.
Is upgrading to Energy Star appliances worth it?
Definitely. Energy Star-rated devices use significantly less power and may qualify for rebates. They also tend to offer better performance and durability, which means long-term value.
Where can I find the best energy saving home improvements?
Start with a home energy assessment to prioritize the best upgrades for your house. This will help identify specific areas to target for the most impactful changes.
This article was drafted using AI technology and then reviewed, fact-checked, and revised by a member of our editorial team.





