
In today’s digitally connected world, seamless internet connectivity is more than a luxury—it’s a necessity. Whether you’re working from home, streaming the latest blockbuster, or diving into an intense online gaming session, the way you connect to the internet can significantly impact your experience. Wi-Fi and Ethernet are the two dominant methods for connecting devices to the web, each with its own advantages and shortcomings. Explore the intricacies of both Wi-Fi and Ethernet so you can determine which connection type aligns best with your needs and lifestyle.
What is Wi-Fi and how does it work
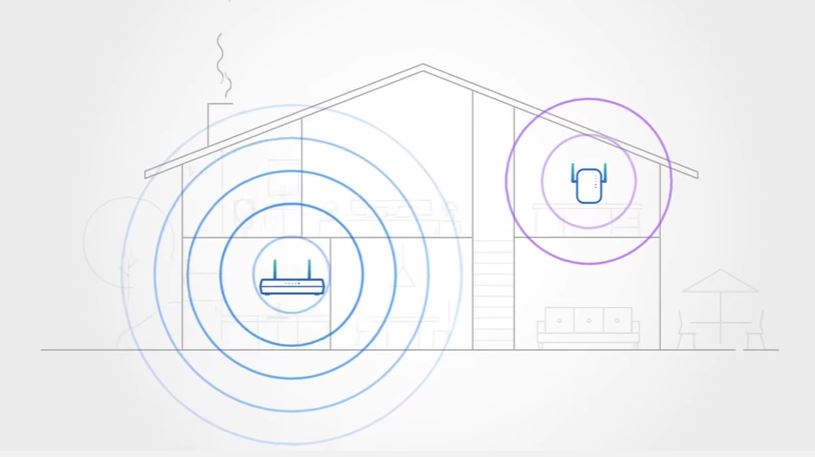
Wi-Fi has its roots in the late 1990s as a solution for wireless data transmission. At its core, Wi-Fi allows devices to connect to a network without physical cables as it operates by transmitting data over radio waves. A device with Wi-Fi capabilities, such as a smartphone or laptop, communicates with a wireless router. This router then fetches the requested data via a wired connection to the Internet and sends it back to the device using the same radio waves. This two-way communication happens at lightning-fast speeds, allowing devices to browse web pages, stream videos, or download files. The beauty of Wi-Fi is that it facilitates this wireless data exchange without the need for any physical connection between the device and the router, offering flexibility and mobility.
Pros and cons of using Wi-Fi
| Pros | Cons |
| Ubiquity: Wi-Fi is widely available, from homes and offices to cafes, parks, libraries, and public transport hubs. | Inconsistent speeds: Depending on the number of connected devices, distance from the router, and potential interference, speeds can fluctuate when using a wireless connection. |
| Simple setup: Most modern devices come with built-in Wi-Fi capabilities, enabling easy and quick connections without additional hardware. | Security risks: Unsecured or poorly secured Wi-Fi networks can be susceptible to eavesdropping and unauthorized access. |
| Device versatility: Wi-Fi is used by a wide range of devices, from laptops and phones to smart home gadgets and wearables. | Limited optimal range: While Wi-Fi can cover a decent range, the signal strength and speed are best when closer to the router. |
| Scalability: With the right equipment, such as Wi-Fi extenders and mesh systems, the range and strength of Wi-Fi can be increased to cover larger areas. | Interference: Other electronic devices, neighbouring Wi-Fi networks, and physical barriers cause signal disruptions and lower signal strength. |
| Guest access: It’s easy to create separate networks or guest access, allowing visitors to connect without compromising main network security. | Potential latency: For real-time applications like gaming or video conferencing, Wi-Fi might introduce slight delays compared to wired connections. |
What is Ethernet?

Ethernet, older than Wi-Fi, was introduced in the 1980s. It allows for data transmission via physical cables, usually referred to as Ethernet cables or CAT cables. Ethernet protocols employ these cables to transmit data. When devices communicate over Ethernet, they dispatch information in small packets. These packets carry both data and address details, ensuring they reach the intended destination. Modern Ethernet setups often involve switches, which guide these data packets efficiently within the network. Thanks to its consistent speeds and robust connection, Ethernet remains the go-to choice for those desiring uninterrupted and high-speed internet engagements such as online gaming, live streaming, and video conferences.
Pros of and cons of using Ethernet
| Pros | Cons |
| Stable connection: Ethernet offers a steady and consistent connection, largely free from the fluctuations Wi-Fi can experience. | Limited mobility: Being tethered to a cable can restrict movement and device placement. |
| High-speeds: Typically, Ethernet provides faster data transfer rates, especially over short distances. | Installation complexity: Proper setup might involve routing cables through walls or ceilings, which can require drilling. |
| Reduced interference: Physical cables aren’t as susceptible to interference from other electronic devices or networks. | Aesthetic concerns: Cables can be unsightly and might not align with everyone’s interior design preferences. |
| Enhanced security: Wired connections are inherently more secure, making unauthorized access more challenging. | Potential for cable damage: Physical cables can wear out, get pinched, or be damaged, requiring replacement. |
| Predictable performance: Ideal for tasks where consistent connection quality is paramount, like online gaming or streaming high-definition content. | Less universal for devices: Not all modern devices come with Ethernet ports, as the trend leans towards wireless solutions. |
Wi-Fi vs. Ethernet: Which one is best?
Because both Wi-Fi and Ethernet each have their pros and cons, here are some key factors to consider when deciding which type of Internet connection you should use:
- Define your online activities: Casual browsing has different connection stability and strength requirements than, for example, 4K video editing or competitive online gaming.
- Examine your space: In a small apartment, Wi-Fi might suffice. However, in a larger home or office, Ethernet could offer consistent connections across various rooms.
- Are you on the move? If you’re someone who loves rearranging furniture or often changes your workspace, being tethered by an Ethernet cable might not be ideal.
- DIY or Pro: Wi-Fi is generally user-friendly for setup. Ethernet, while not too complicated, might require a bit more technical know-how to set up correctly.
- Financial implications: An initial Ethernet setup might be more costly, especially if professional installation is needed. However, with Wi-Fi, you might find yourself investing in extenders or mesh systems for better coverage.
- Safe and secure: If your data is sensitive, especially in business settings, Ethernet usually has the upper hand in security.
- Quality over quantity: While Wi-Fi offers convenience, Ethernet often promises better speed and consistency, especially for data-heavy tasks.
Get connected with the right networking solution for you
Both Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections have their strengths and weaknesses. Deciding which one is best for your needs is all about understanding your needs and evaluating your environment. Take a moment to assess your unique situation, and you’re sure to make a decision that keeps your online world spinning smoothly.
This article was drafted using AI technology and then reviewed, fact-checked, and revised by a member of our editorial team.




