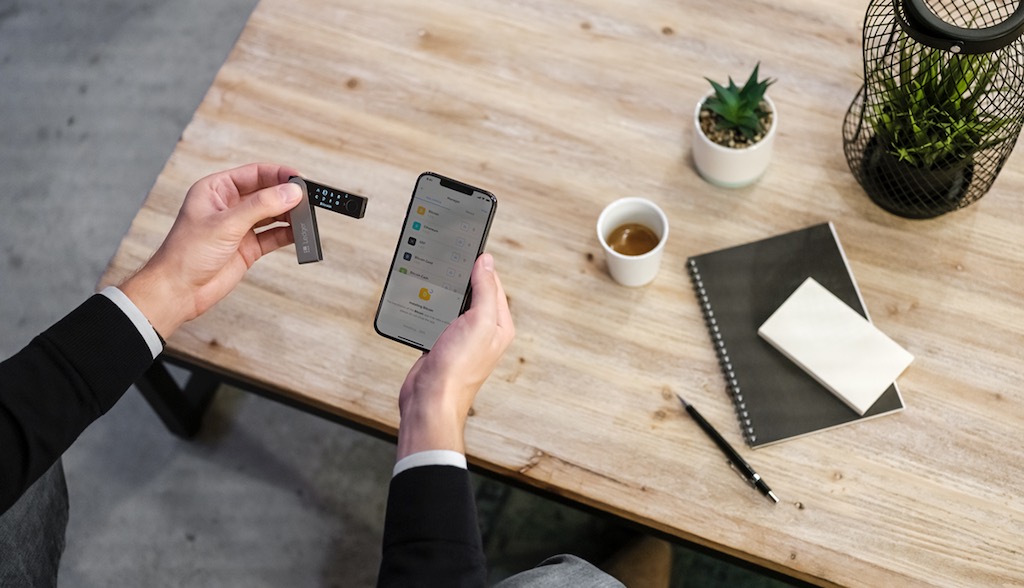

If you have entered the digital world of cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, you may want a crypto wallet. Crypto wallets are designed to securely store your cryptocurrency in either an online location (hot wallets) or in a local, hardware device (cold wallets). Whether you’re just buying crypto currency for an investment, actively trading it, or using crypto for transactions, understanding the pros and cons of the different types of crypto wallets is important so you make the right, secure storage decision for your needs.
Introduction to crypto and blockchain
A blockchain is a ledger that’s shared online. It records transactions like the buying and trading of cryptocurrencies; multiple transactions occurring within a given time-period are stored in “blocks.” Each transaction is recorded just once within the block, and a block can’t be edited or modified once it’s recorded. The blocks form a permanent, secure chain of data that’s updated in real time as transactions take place—forming a blockchain.
 Cryptocurrency is a form of currency that exists digitally instead of physically. It uses encryption to secure transactions. Each cryptocurrency (there are thousands of them with the first with the most widely known being Bitcoin) is a peer-to-peer system that records all transactions on a distributed public ledger. Crypto coins are generated or “mined” by computers that solve complex mathematical questions. However, most owners buy their coins from brokers and exchanges since crypto mining rigs are costly to set up and expensive to operate.
Cryptocurrency is a form of currency that exists digitally instead of physically. It uses encryption to secure transactions. Each cryptocurrency (there are thousands of them with the first with the most widely known being Bitcoin) is a peer-to-peer system that records all transactions on a distributed public ledger. Crypto coins are generated or “mined” by computers that solve complex mathematical questions. However, most owners buy their coins from brokers and exchanges since crypto mining rigs are costly to set up and expensive to operate.
When you buy cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, the reality is you don’t really own a physical asset. What you own is a private key that provides access to your digital holdings on a blockchain. That private key is required to access your crypto assets, buy and sell crypto, and to authorize any crypto-related transactions.
What is cryptocurrency and why does it need special storage?
Cryptocurrency is a purely digital asset. There is no physical version like paper money. All records of your ownership and transactions are stored on a blockchain. Access is gained using a private key, which like the currency itself is also not physical. A private key is a long set of hundreds of numbers: similar to a very, very long password. If you lose your private key for a cryptocurrency, you lose access to your holdings irrecoverably. If you are hacked and someone gains control of your private key, they gain full access to your holdings. An analogy is a safe deposit box: if someone gets your key, they can transfer the contents from your box to their pocket.
 Because of the critical importance of your private key—which is required to do everything from buying crypto to using your crypto holdings to make a purchase—it should have special storage. The storage for cryptocurrency is called a crypto wallet. Unlike a traditional wallet which holds physical currency, a crypto wallet does not “store” digital coins. Instead, it stores your private key, which unlocks access to your crypto account.
Because of the critical importance of your private key—which is required to do everything from buying crypto to using your crypto holdings to make a purchase—it should have special storage. The storage for cryptocurrency is called a crypto wallet. Unlike a traditional wallet which holds physical currency, a crypto wallet does not “store” digital coins. Instead, it stores your private key, which unlocks access to your crypto account.
Technically, you could write down your private key on a piece of paper. However, that is easy to lose, damage, or get stolen. Surprisingly the loss of crypto in this way has been a big problem. According to a New York Times report, there is an estimated $140 billion in Bitcoin alone that is currently inaccessible because the owners have lost their private keys. You don’t want to find yourself in that situation. Crypto wallets solve this problem in a variety of ways similar to those that allow you access to other assets you own, like a bank account, etc. This will be explained in more details after you learn about the two main kinds of crypto storage: hot and cold wallets.
Different kinds of crypto storage
There are two different kinds of crypto storage: hot wallets and cold wallets. Both are designed to secure digital assets, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. People who are new to acquiring crypto currency or other digital assets need to learn about the pros and cons to make the right decision for their needs and so they understand how much risk they assume once they choose a wallet. Importantly, many crypto investors have a combination of hot and cold wallets rather than one or the other.
Hot wallets
Hot wallets are those that are physically connected to the internet. There are various types of hot wallets including:
- Web wallet (your private key is stored on a third-party server for use on a web-based service or exchange)
- Desktop wallet (your private key is downloaded and stored on your PC’s hard drive, but remains vulnerable due to the PC’s internet connection)
- Mobile wallet (your private key is stored on a mobile app on your smartphone)
Hot wallets conveniently store your assets for easy access and on-demand, virtually instant transactions. However, these advantages come at a cost as this form of storage can be vulnerable to attack by internet hackers.
Cold wallets
Cold wallets are not physically connected to the internet. As such they keep your private keys offline, out of reach of internet hackers. This advantage comes with the disadvantage that transactions may require more steps to complete than with a hot wallet. Additionally, if you lose a physical cold wallet, your assets are gone in the same way that if you lose a physical dollar bill it is gone.
The most basic form of a cold wallet is a paper wallet: essentially this is a paper document on which is printed the keys to your assets. It has the advantage of not being connected to the internet, but the disadvantage that it is on paper, which can easily to tossed, destroyed, or rendered illegible—thereby making your assets irretrievable. A better form of cold wallet is a hardware wallet.
Why are hardware wallets the most recommended storage solution for crypto
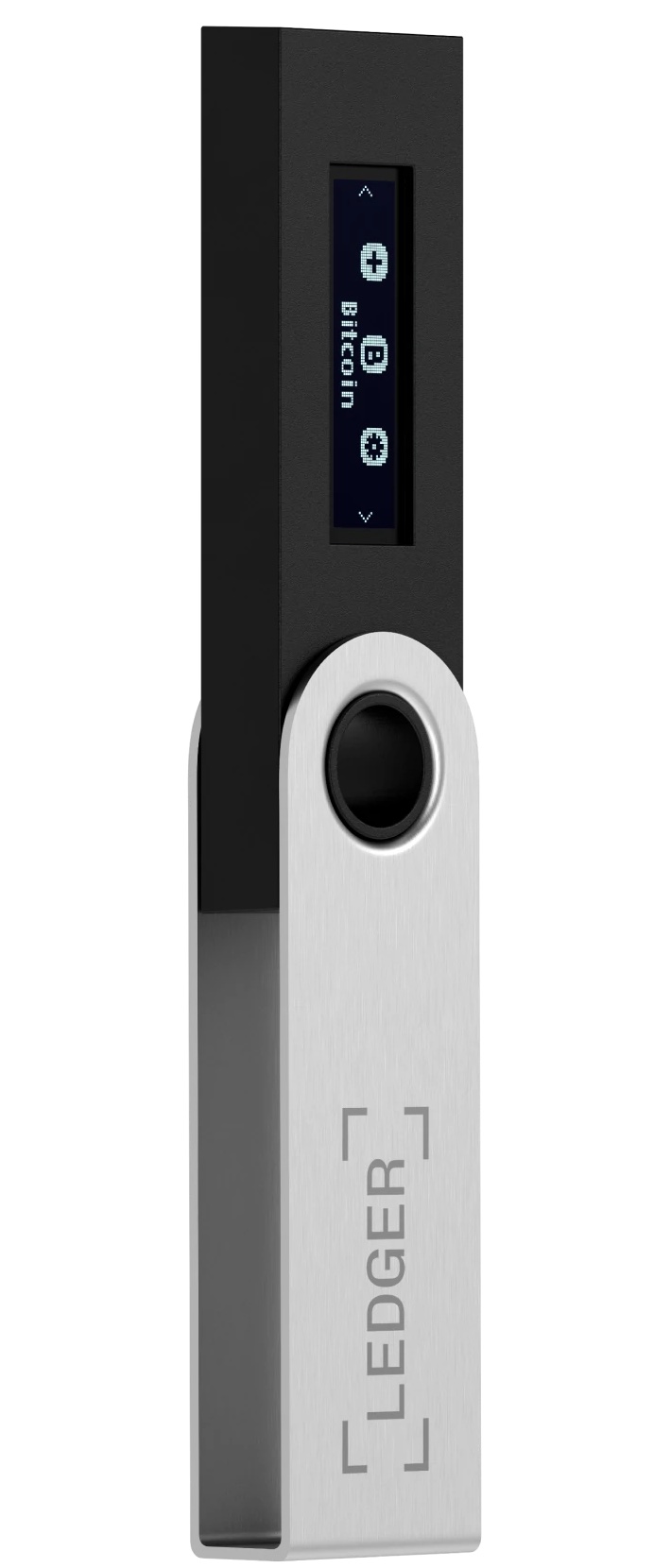 Hardware wallets are a popular form of cold wallet. They keep your crypto keys secure on a portable device, similar to a thumb drive. To use them, they are connected to a PC or mobile device. You then initiate a secure, temporary connection to the web for a transaction. This resembles the temporary, secure transactions you are familiar with for online banking. During the transaction, the encryption protocols protect you, after the transaction, you remove the device from the computer so the internet no longer has access.
Hardware wallets are a popular form of cold wallet. They keep your crypto keys secure on a portable device, similar to a thumb drive. To use them, they are connected to a PC or mobile device. You then initiate a secure, temporary connection to the web for a transaction. This resembles the temporary, secure transactions you are familiar with for online banking. During the transaction, the encryption protocols protect you, after the transaction, you remove the device from the computer so the internet no longer has access.
Some hardware wallets have a display that shows important information such as the name of the cryptocurrency being used and transaction amounts for visual confirmation.
Because of the inherent advantages and disadvantages of hot and cold wallets, experienced crypto owners often use a dual approach. They keep a small crypto balance in a hot wallet for convenient access for purchases and transactions, while protecting the bulk of their holdings with a cold crypto wallet.
One of the best solutions to crypto security is offered by products like the Ledger Nano S and Ledger Nano X. These are hardware crypto wallets with cold storage and advanced security chips. They ensure your private key is safe from hackers. However, they also include access to the Ledger Live app for crypto currency management, and they are compatible with a wide range of the most popular crypto currencies.
You connect your Ledger Nano crypto wallet to your device and enjoy security and the convenience of using a hot wallet.
Used crypto wallets
Given what’s at stake, it is risky to buy a used crypto wallet and or one from an unknown retailer or manufacturer. Some fake wallets have been found that look legitimate, but enable cybercriminals to access your private key and drain your cryptocurrency account.
You really should have a crypto wallet backup
For many years we have all heeded the advice to backup important personal digital information on an external hard drive. For example, if you want to make sure your precious photos remain accessible for many years, you must back them up. Digital files like your family photo albums are irreplaceable. Even data that might be stored online can be a pain to download and reintegrate. It’s a lot easier to do a complete restore from a backup.
The same logic holds true for a crypto wallet. Ultimately, a crypto wallet is built around electronics and memory chips. Failures are uncommon, but they happen. It’s also possible for you to physically lose your crypto wallet. These devices come with recovery passwords, but it’s possible to lose this as well.
Therefore, many crypto investors keep a backup crypto wallet as a smart precaution. If you lose your main crypto wallet, the backup ensures you don’t lose access to your crypto holdings. If you are just beginning your crypto journey, build good habits from the beginning, before your initial assets grow. The fact is that hardware tokens are not expensive, setting them up is not arduous, and learning how to use them takes very little time.
Take the next step
 Now that you know what’s involved with crypto wallets and understand why you should be using a hardware wallet to secure your crypto assets, it’s time to pick the model that’s best for your needs. You’ll find the crypto wallets from the most trusted brands including Ledger at Best Buy.
Now that you know what’s involved with crypto wallets and understand why you should be using a hardware wallet to secure your crypto assets, it’s time to pick the model that’s best for your needs. You’ll find the crypto wallets from the most trusted brands including Ledger at Best Buy.
Disclaimer
Information contained or referenced herein is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended to provide, and should not be relied upon as, investment or other advice. You should perform your own research and understand all risks associated with crypto currency before making purchasing decisions.
Sources used:
https://www.wired.com/story/how-to-choose-set-up-crypto-wallet/
https://www.ledger.com/academy/crypto/where-are-my-coins
https://get.bitbuy.ca/guides/crypto-wallet-security-101-cold-storage-guide
https://cointelegraph.com/bitcoin-for-beginners/bitcoin-wallets-a-beginners-guide-to-storing-btc
https://www.ibm.com/topics/what-is-blockchain
https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/what-is-cryptocurrency
https://www.nytimes.com/2021/01/12/technology/bitcoin-passwords-wallets-fortunes.html
https://www.ledger.com/academy/hardwarewallet/increase-your-security-with-a-backup-device



